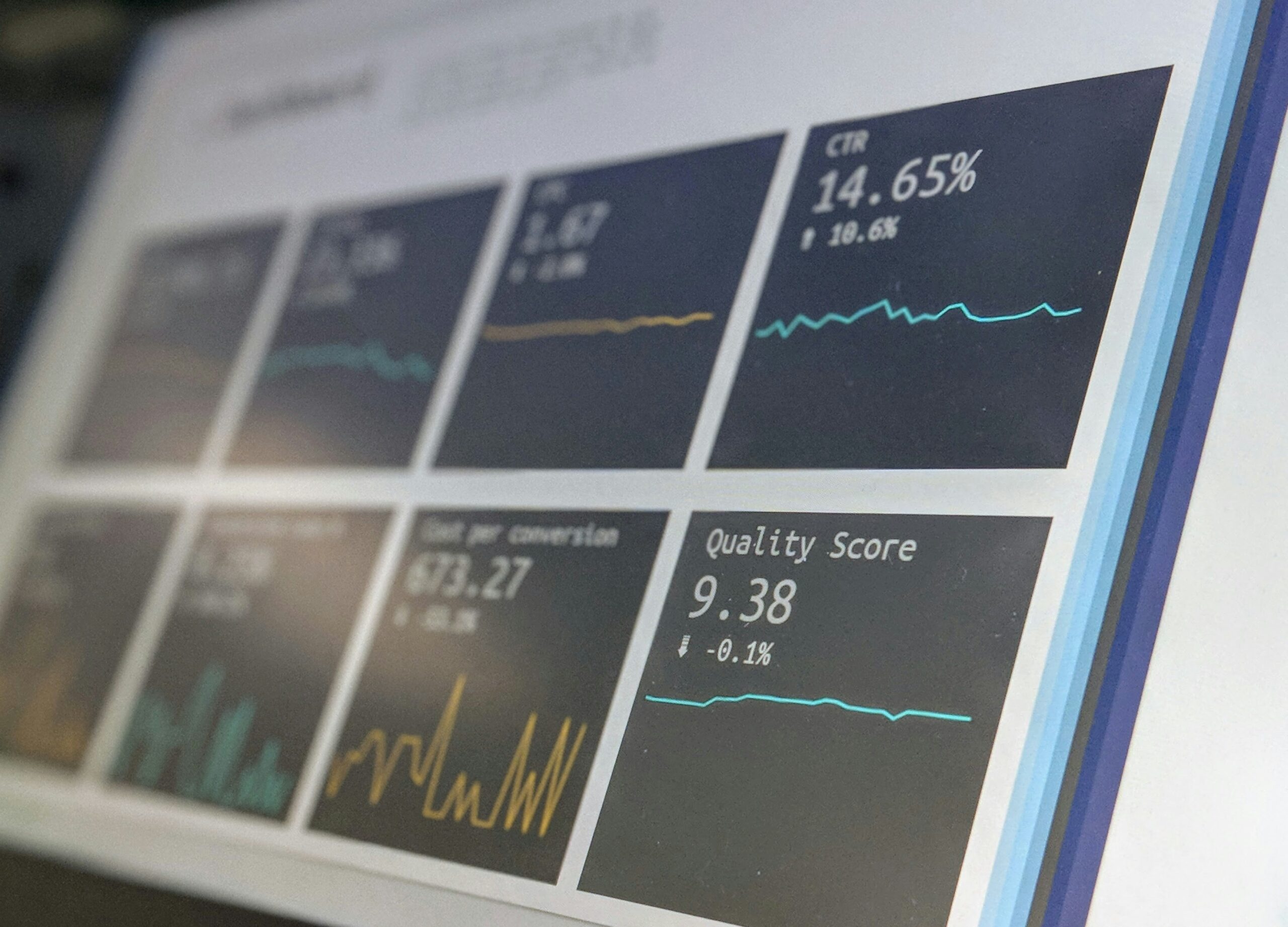
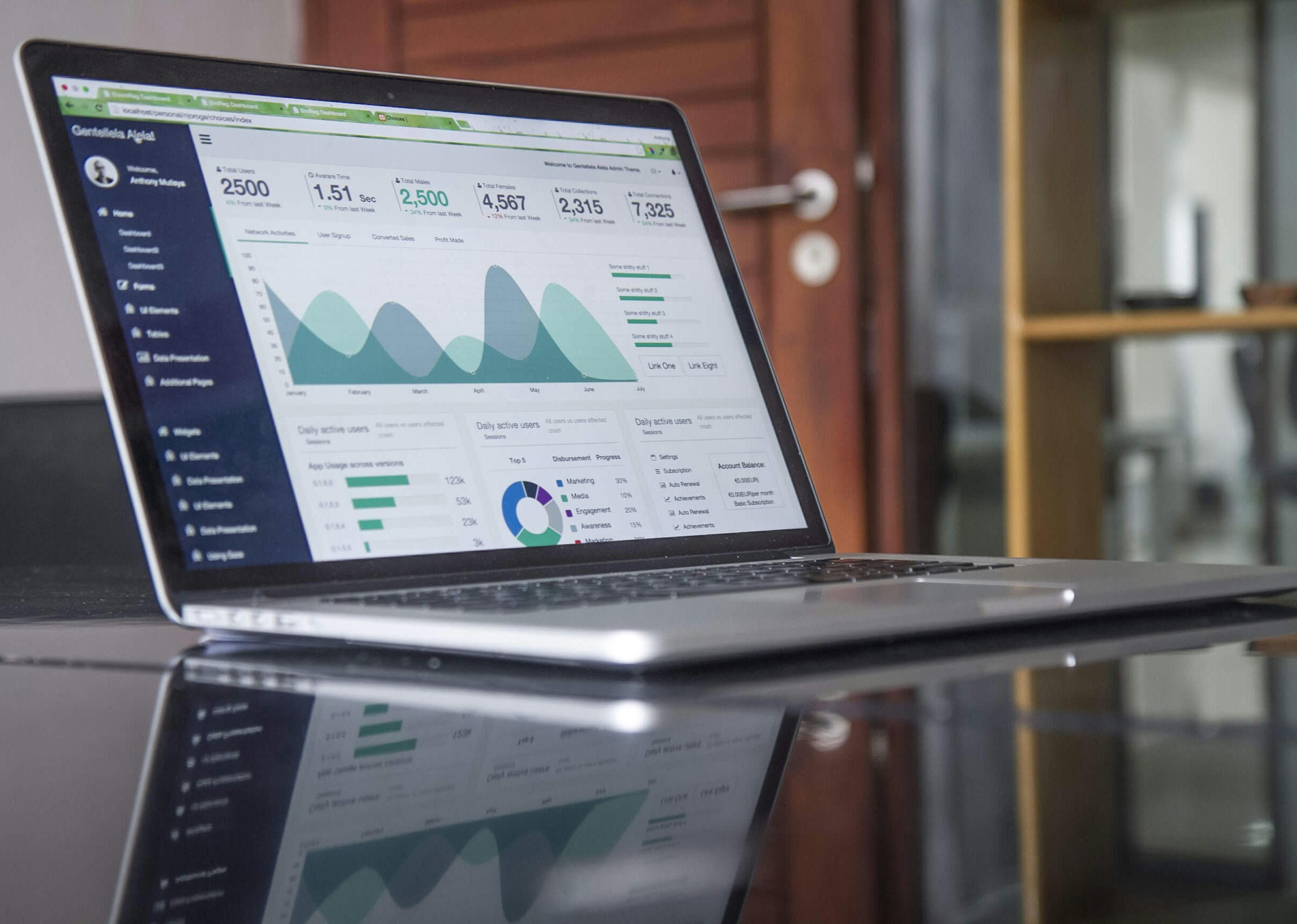
Introduction to Feasibility Analysis Feasibility analysis is a comprehensive evaluation process aimed at determining whether a proposed project is worth the investment or not. This analysis requires in-depth study...
Introduction to Bookkeeping Services Bookkeeping services are a vital part of the accounting system of any organization, as they represent the basic basis on which daily financial operations are built. through...
FANNKLE RETURN AT OUR RULE AS WHEN ACTING OFFICE IN IT
Introduction to Tax Auditing
Tax auditing is one of the fundamental processes that contributes to ensuring tax compliance and verifying the accuracy of information provided by companies and individuals to tax authorities. The aim of tax auditing is to ensure that taxpayers correctly report their income, deductions, and other financial data in accordance with tax laws. Through this process, tax authorities can detect potential errors, discrepancies, or fraud, and take corrective measures to safeguard the integrity of the tax system.
Corporate tax is one of the important financial tools used by governments to generate revenue by imposing taxes on the profits earned by business entities. The significance of corporate tax is reflected in its role as a major source of public funding,
Introduction to Value-Added Tax (VAT)
Value-Added Tax (VAT) is one of the most important government financing tools worldwide. This tax serves as a mechanism for funding government budgets by imposing charges on the added value of goods and services at each stage of production or distribution. VAT is collected incrementally throughout the supply chain but is ultimately borne by the end consumer, making it a significant source of revenue for many governments.
Introduction to Tax Planning
Tax planning is a vital strategic process aimed at reducing the financial burden of taxes for both individuals and businesses. This process requires a thorough understanding of various tax laws and regulations to identify opportunities for minimizing tax liabilities while ensuring full compliance with legal requirements. Effective tax planning helps optimize financial outcomes by taking advantage of deductions, credits, and tax-efficient structures available under the law.
Introduction to Value-Added Tax (VAT)
Value-Added Tax (VAT) is a modern tax system that imposes a tax on the added value at each stage of production and distribution. The primary goal of VAT is to create a consistent and fair method of taxation by ensuring that taxes are applied to the value added at each phase of the supply chain, from the manufacturer to the final consumer.
Value-Added Tax (VAT) and Its Importance for Businesses
Value-Added Tax (VAT) is one of the most significant indirect taxes imposed on the consumption of goods and services. It is applied in many countries around the world as a reliable source of government revenue. VAT is levied at each stage of the supply chain, from production to final sale, but the end consumer ultimately bears the cost. Businesses act as intermediaries, collecting VAT from customers and remitting it to the tax authorities.
Economic crises such as pandemics, natural disasters, and political conflicts are some of the biggest challenges businesses face. Among these challenges, a liquidity crisis emerges as one of the most dangerous threats that can weaken a company's ability to meet its financial obligations. A liquidity crisis occurs when a business faces a shortage of cash flow needed to cover its day-to-day operational expenses or repay its debts, which can ultimately lead to financial distress or even bankruptcy.